VLOOKUP in Excel – The Massive Guide
The term “Vertical” signifies that it can be used to look up values vertically i.e. it can be used to look up values inside a column.
You can also read my previous post: “How to alphabetize in Excel”, there I have used VLOOKUP for sorting a list.
Note: This is a long post over 2500+ words, you will feel comfortable navigating it the using below jump links.
- Definition of VLOOKUP in Excel
- What are the uses of Vertical Lookup Function?
- Syntax of VLOOKUP Function
- Few Important points about Vertical Lookup function
- How to Use VLOOKUP?
- 5 Beginner level examples of VLOOKUP function
- Few Practical Examples of Vertical Lookup function
- How to Use VLOOKUP in VBA
- How to return multiple columns from a VLOOKUP
- Negative VLOOKUP
- Creating a multiple criteria VLOOKUP
Definition of VLOOKUP in Excel:
According to Microsoft Excel VLOOKUP can be defined as a function, “that looks for a value in the leftmost column of a table, and then returns a value in the same row from a column you specify. By default the table must be sorted in an ascending order.”What are the uses of Vertical Lookup Function?
This function is mostly used for following tasks:- To look up a single or a set of values from a data sheet.
- To add a column to a datasheet from some other table, based on some unique (attribute)s.
Syntax of VLOOKUP Function:
Its syntax is as follows:=VLOOKUP( lookup_value, table_array, column_index, range_lookup )lookup_value’ specifies the value to be searched inside the ‘table_array’. It can either be a value or a reference.‘
table_array’ is the range with two or more columns. ‘table_array’ argument can receive a range reference or a named range. The leftmost column of this range must contain the ‘lookup_value’.‘
column_index’ is the relative index of the column whose value needs to be returned by the VLOOKUP function. A ‘column_index’ 1 would return values from the first column in the ‘table_array’ similarly ‘column_index’ 2 would return values from the second column in the ‘table_array’.‘
range_lookup’ is a Boolean value that specifies whether
you want VLOOKUP to find an exact match or an approximate match. If its
value is ‘True’ then either an approximate or an exact match will be
returned. Here, if an exact match is not found, the next value that is
less than ‘lookup_value’ is returned. If its value is ‘False’ then only exact match will be returned.Few Important points about Vertical Lookup function:
- VLOOKUP function performs a case-insensitive lookup.
- VLOOKUP in Excel returns a ‘#N/A’ if it is not able to find the ‘
lookup_value’ inside the ‘table_array’. - It returns a ‘#VALUE!’ error if the value of ‘
column_index’ is less than 1. - It returns a ‘#REF!’ error if the value of ‘
column_index’ is greater than the number of columns in the ‘table_array’. - The default value of ‘
range_lookup’ is TRUE. So, it is better to omit this argument in case you need to perform either an approximate or an exact match. - Vertical Lookup allows you to use wildcard characters in the ‘
lookup_value’ argument. We will discuss it later in this article.
How to Use VLOOKUP?
Before understanding how to use Vertical Lookup function, you must understand what its objective is. Let’s try to understand this with a sample problem.Suppose we have a table as shown below.
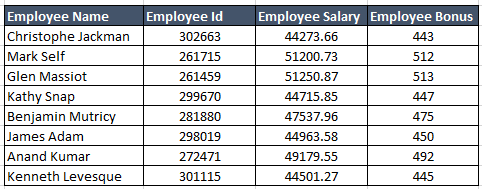
Objective: Our objective is to find the salary of any particular employee (say: Benjamin Mutricy) based on his name.
Solution: Now, lets try to apply a VLOOKUP to find the solution.

lookup_value: This is the value based on which the lookup is to be performed. In our case lookup_value is in the cell B4 i.e. “Benjamin Mutricy”.
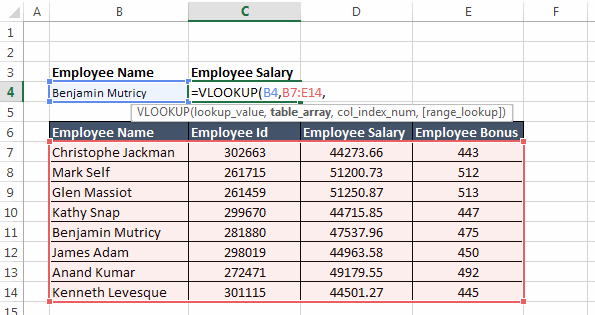
table_array: This is the range of the table from which the values are to be fetched. Note that this ‘
table_array’ should always contain ‘lookup_value’ in its leftmost column.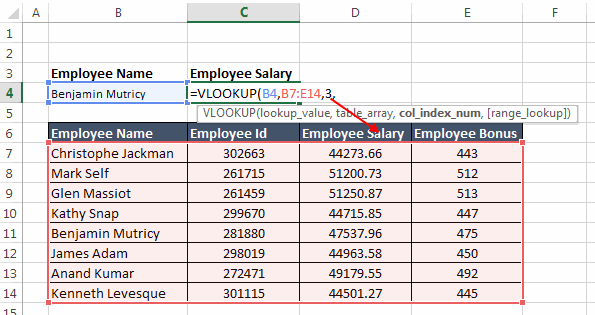
col_index_num: This specifies the positional reference of the column that you want the VLOOKUP to return.
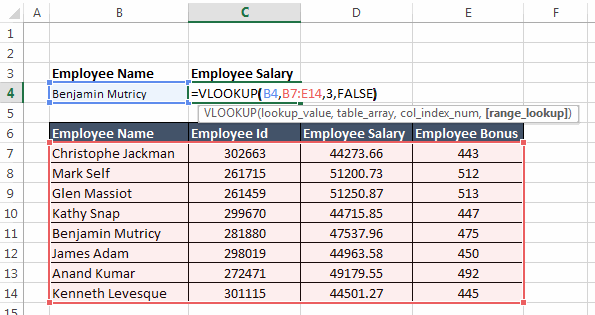
range_lookup: This specifies that weather the match should be exact or approximate. FALSE specifies exact match.
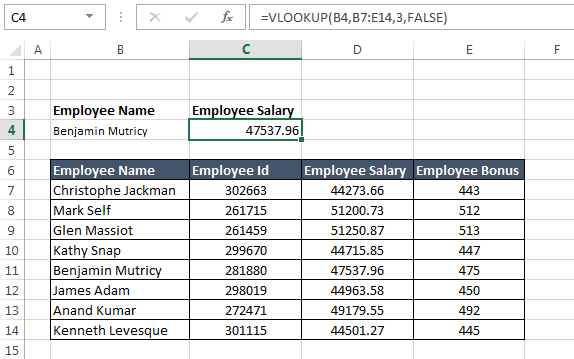
So, in this case the VLOOKUP function would be:
=VLOOKUP(B4,B7:D14,3,FALSE)5 Beginner level examples of VLOOKUP function:
Now let’s move to some examples:Example 1: In this example we have a list of students with their scores. Now, here we need to find the score of a student with the First Name ‘Vincent’.
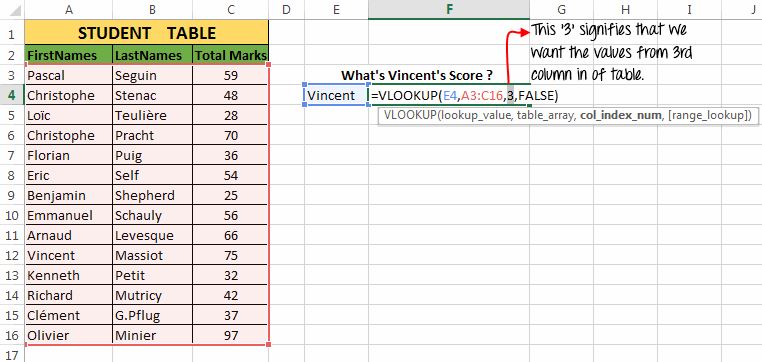
To find the solution to our problem, we have used the vertical lookup as:
=VLOOKUP(E4,A3:C16,3,FALSE) and it gives the result 75.Explanation:
- The first argument to the function i.e. ‘
lookup_value’ = E4 (Reference of “Vincent”) - Second argument i.e. ‘
table_array’ = A3:C16 (Range of student table) - Third argument i.e. ‘
column_index’ = 3 (the column number whose value the VLOOKUP function should return) - Fourth argument i.e. ‘
range_lookup’ = FALSE (Signifies that we only want the exact match)
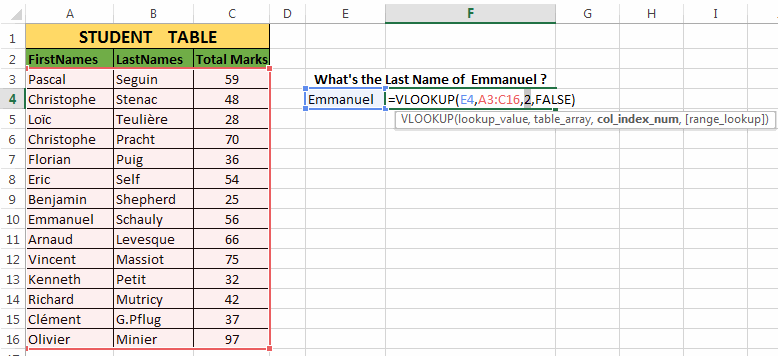
So, we will use the VLOOKUP as:
=VLOOKUP(E4,A3:C16,2,FALSE) and it results into “Schauly”Explanation:
- The first argument to the function i.e. ‘
lookup_value’ = E4 (Reference of “Emmanuel”) - Second argument i.e. ‘
table_array’ = A3:C16 (Range of student table) - Third argument i.e. ‘
column_index’ = 2 (the column number whose value the VLOOKUP function should return) - Fourth argument i.e. ‘
range_lookup’ = FALSE (Signifies that we only want the exact match)
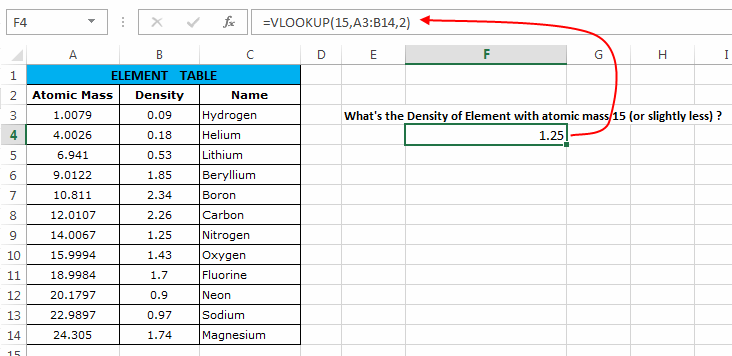
Here we have to find the Density of an Element whose atomic mass is 15 or slightly less.
Now, here we can use the vertical lookup formula as:
=VLOOKUP(15,A3:B14,2) which results into 1.25.Explanation:
- The first argument to the function i.e. ‘
lookup_value’ = 15 (Atomic Mass to be searched) - Second argument i.e. ‘
table_array’ = A3:B14 (Range of Element Table) - Third argument i.e. ‘
column_index’ = 2 (the column number whose value the vertical lookup function should return) - Fourth argument i.e. ‘
range_lookup’ is omitted and hence its value is true. So, first it searches 15 in the Atomic Mass column but when it fails to find 15, it returns the density of element slightly less than 15.
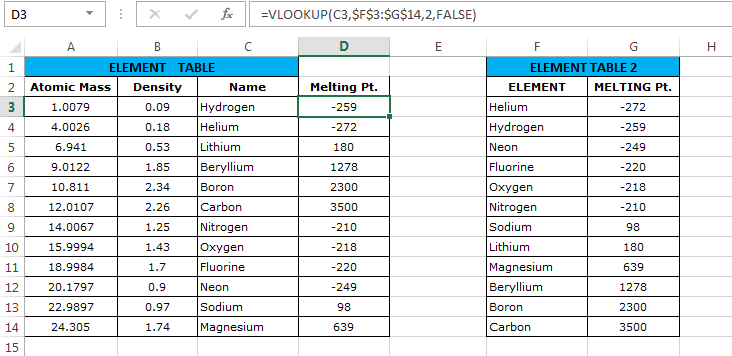
This can be done by using the formula:
=VLOOKUP(C3,$F$3:$G$14,2,FALSE)After applying this formula for the first element we have to drag the formula below (using the fill handle) for other elements.
Explanation:
- The first argument to the function i.e. ‘
lookup_value’ = C3 (Reference for first element) - Second argument i.e. ‘
table_array’ = $F$3:$G$14 (Range of Element Table 2) – If you are wondering what are these ‘$’ signs along with the table reference, then you should read this post. - Third argument i.e. ‘
column_index’ = 2 (the column number whose value the vertical lookup function should return) - Fourth argument i.e. ‘
range_lookup’ = FALSE (Signifies that we only want the exact match)
Example 5: In this example we will use wildcard operators along with Vertical Lookup. Here we have to find the score of the student whose first name starts with ‘A’.
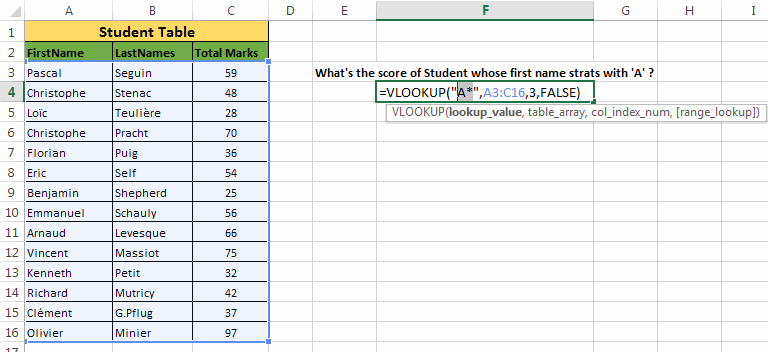
=VLOOKUP("A*",A3:C16,3,FALSE) which gives a result 66.Explanation:
Generally, we can use following two wildcard operators with VLOOKUP function.
| Wildcard | Description |
|---|---|
| ‘?’ | Denotes any single character. |
| ‘*’ | Denotes any number of characters |
Note: Simply placing the tilde sign (~) before any wildcard character tells Excel that the wildcard character (‘*’ or ‘?’) should be treated as a string and not as wildcard operator.
- The first argument to the function i.e. ‘
lookup_value’ = “A*” (Any word starting with ‘A’ alphabet) - Second argument i.e. ‘
table_array’ = A3:C16 (Range of Student Table) - Third argument i.e. ‘
column_index’ = 3 (the column number whose value the vertical lookup function should return) - Fourth argument i.e. ‘
range_lookup’ = FALSE (Signifies that we only want the exact match)
Few Practical Examples of Vertical Lookup function:
Now let’s see some practical examples of VLOOKUP Function:Example 6: Let’s say we have a list named “Child List” and another list with the name “Master list”. Now, using Vertical lookup we need to find if all the items in “Child List” are also present in the “Master list”.
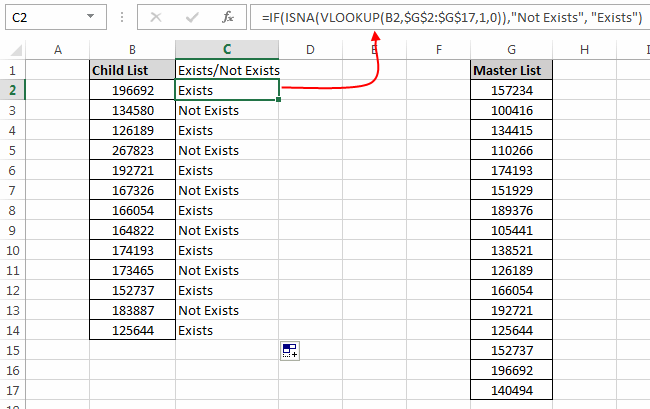
In such a case we will use the formula:
=IF(ISNA(VLOOKUP(B2,$G$2:$G$17,1,0)),"Not Exists", "Exists")This formula uses If Statement, ISNA function and VLOOKUP.
Explanation:
Here IF statement checks whether the output of VLOOKUP function is #NA Error or not. IF the output is #NA error, then it means that current child list item is not present in the master list. And hence the IF statement writes “Not Exists” in front of it, however if the item is present in the master list then it writes “Exists”.
Example 7: Translating scores to grades using vertical lookup. Let’s say we have a table with student scores and now we have to assign them a grade based on their scores.
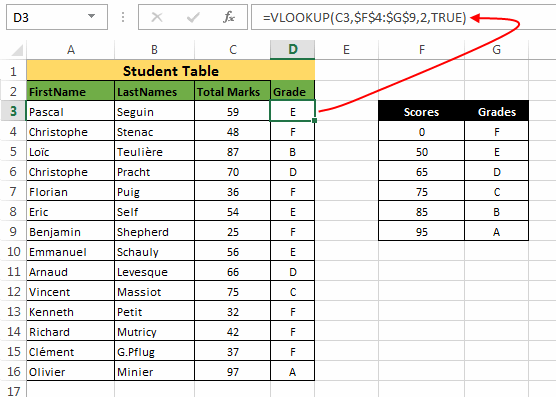
For this we can use a VLOOKUP as:
=VLOOKUP(C3,$F$4:$G$9,2,TRUE) and then drag this formula to below cells.Explanation:
- The first argument to the function i.e. ‘
lookup_value’ = C3 (Reference for first element) - Second argument i.e. ‘
table_array’ = $F$4:$G$9 (Range of scores and grades table) - Third argument i.e. ‘
column_index’ = 2 (the column number whose value the VLOOKUP function should return) - Fourth argument i.e. ‘
range_lookup’ = True (It matches both the exact values and values slightly lesser)
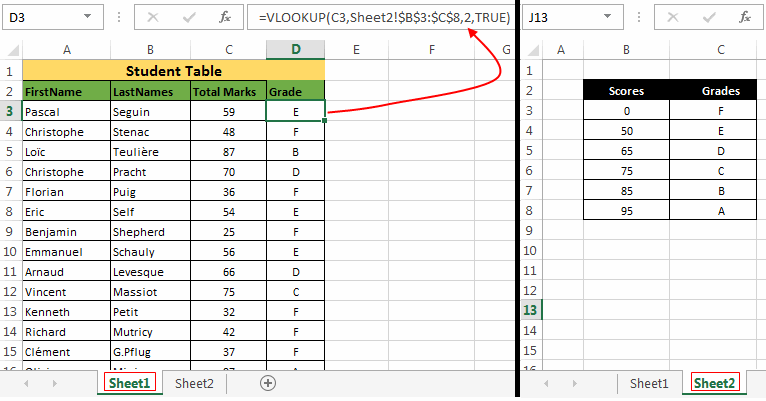
In this example the “Student Table” is on ‘Sheet1’ while the “Grade and Score table” is on the ‘Sheet2’. So you can use a VLOOKUP as:
=VLOOKUP(C3,Sheet2!$B$3:$C$8,2,TRUE)Explanation:
- The first argument to the function i.e. ‘
lookup_value’ = C3 (Reference for first element) - Second argument i.e. ‘
table_array’ = Sheet2!$B$3:$C$8 (Range of scores and grades table which is present on Sheet2) - Third argument i.e. ‘
column_index’ = 2 (the column number whose value the vertical lookup function should return) - Fourth argument i.e. ‘
range_lookup’ = True (It matches both exact and values slightly lesser)
See the below animation for more details:

How to Use VLOOKUP in VBA:
VLOOKUP function can also be used in VBA. Below is a sample code:- Sub Vertical_lookup_test()
- Dim Result As Variant
- Dim myVal As String ' Can be Integer, long, double etc.
- Dim Rng As Range
- Dim Clm As Integer
- Set Rng = ActiveSheet.Range("A:E") ' Set Range
- myVal = "Florian" ' Value to be searched
- Clm = 3 ' Column to be fetched
- Result = Application.VLookup(myVal, Rng, Clm, False)
- If IsError(Result) Then
- Result = "Not found!"
- End If
- MsgBox Result
- End Sub
1. Change
Set Rng = ActiveSheet.Range("A:E") to the range that you wish to use.2. Change
myVal = "Florian" to the value that you want the vertical lookup to search. You can also use the InputBox function to get this value from user during the runtime.3. Change
Clm = 3 to the column that you the VLOOKUP to fetch.How to return multiple columns from a VLOOKUP?
Till now we have seen VLOOKUP functions that only returns a single column. But there are times when you need a VLOOKUP function to return multiple columns from the specified row.So, you have to make a VLOOKUP formula that can fetch multiple columns. The basic idea behind this is, we will use VLOOKUP as an array function.
Follow the below steps to use this:
Suppose we need to fetch all the details of “Florian” so we will proceed as:
1. Select the cells (cells equal to the number of columns that you wish to fetch) where you wish to populate the VLOOKUP results.
2. Next, without clicking anywhere else type the formula:
VLOOKUP("Florian",A:D,{1,2,3,4},FALSE) in the Formula bar. The third argument i.e. {1,2,3,4} specifies the columns that need to be fetched.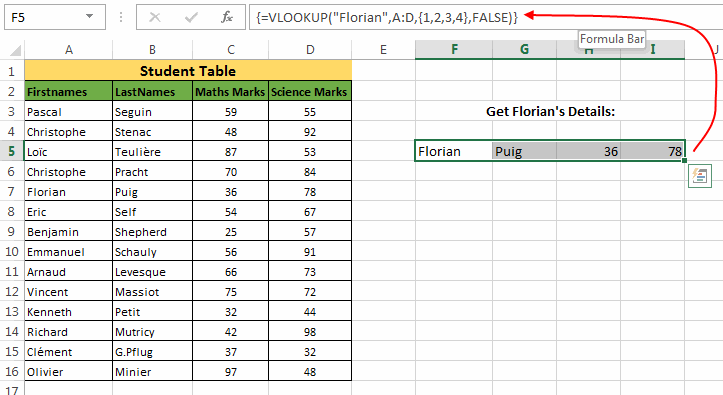
3. After this simply hit the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys. This will enclose the above formula in curly brackets and the cells that you had selected will show the fetched columns.
Negative VLOOKUP:
In all the previous examples you must have seen that we have always used a ‘lookup_value’ that is present in the leftmost column of the range. So, the question arises, can we use a ‘lookup_value’ which is not in the leftmost column? 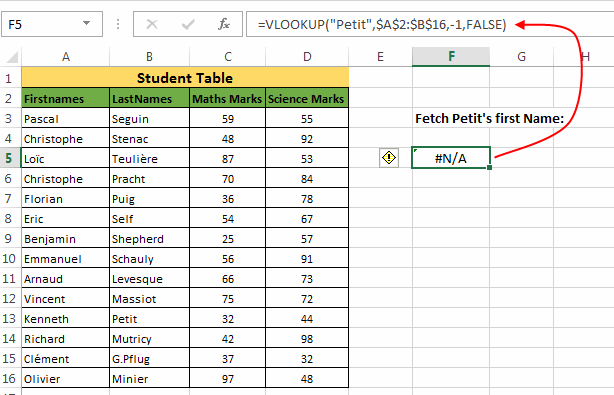
See what happens when your ‘
lookup_value’ is not on the leftmost side, and you enter a negative ‘column_index’ hoping to fetch the value to the left of ‘lookup_value’.A simple way to do this is by building a user defined function (UDF). This function internally doesn’t use VLOOKUP but it can give you desired results. Below is the UDF:
- Function NEGATIVE_VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array As Range, col_index_num As Integer, CloseMatch As Boolean)
- Dim RowNbr As Long
- RowNbr = Application.WorksheetFunction.Match(lookup_value, table_array.Resize(, 1), CloseMatch)
- NEGATIVE_VLOOKUP = table_array(RowNbr, 1).Offset(0, col_index_num)
- End Function
How to use this Negative VLOOKUP UDF:
Let’s understand how to use this function. In our example we have a Student Table and we have to find the first name of “Petit”.
So, we will use this formula as:
=NEGATIVE_VLOOKUP("Petit",B:B,-1,FALSE)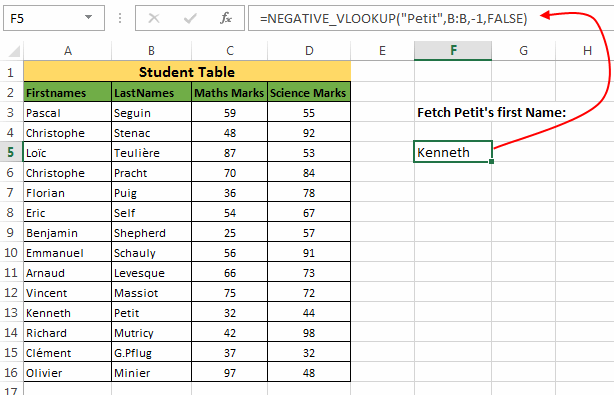
Explanation:
- The first argument to this UDF is the ‘
lookup_value’. - Second argument is the range where this UDF should search for ‘
lookup_value’. - Third argument is the positional reference of the column which this UDF should return.
- Last argument is the Boolean value specifying exact or approximate match.
=NEGATIVE_VLOOKUP(98,D:D,-3,FALSE)Creating a multiple criteria VLOOKUP:
While doing data analysis in excel sometimes you may run into situations where you need to apply a VLOOKUP based on two keys (i.e. based on two ‘lookup_values’).For example: We have a Student table as shown in the below image. Now, as you can see that there are two students with First Name “Christophe” (at A4 and A6). So, applying a VLOOKUP on first name can cause inconsistency. Hence we will apply a VLOOKUP based on both First name as well as the Last name.
But as we know that VLOOKUP in Excel can only have a single ‘
lookup_value’. So we need to create a helper column by appending first name and last name as =A3&" "&B3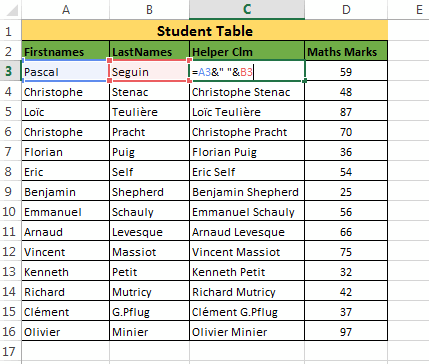
Now, we have combined two keys together and hence this new key column would contain unique values.
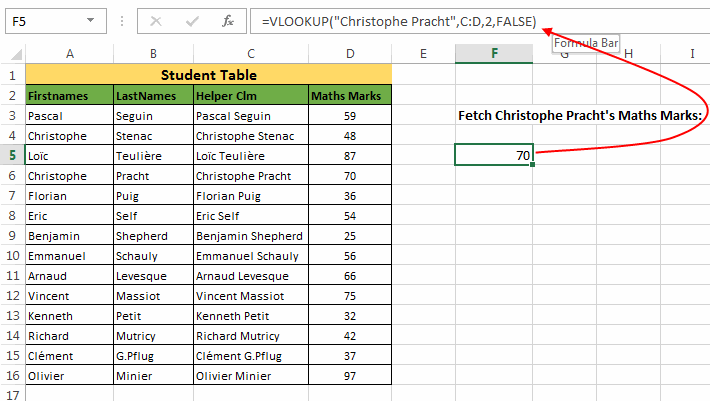
Next, we can simply apply a Vertical lookup as:
=VLOOKUP("Christophe Pracht",C:D,2,FALSE)So, this was all about VLOOKUP in Excel. Do read this post if this long article has bored you and don’t forget to share your ideas and thoughts with us in the comments section.



No comments:
Post a Comment